Traffic Portal - Using
Traffic Portal is the official Traffic Control UI. Traffic Portal typically runs on a different machine than Traffic Ops, and works by using the Traffic Ops API. The following high-level items are available in the Traffic Portal menu.
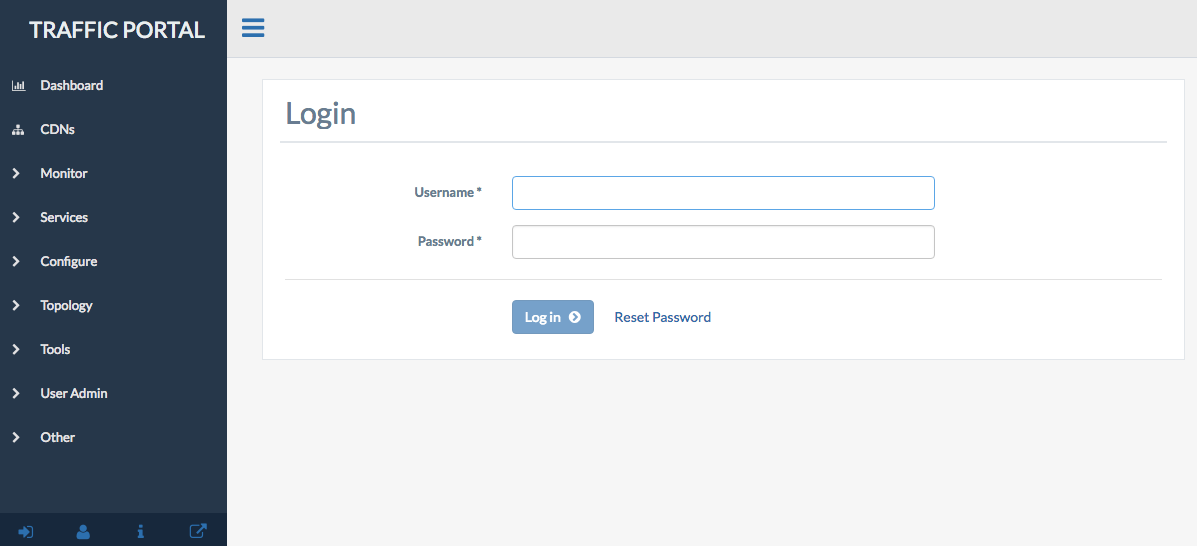
Fig. 4 Traffic Portal Start Page
Change Logs
At the top-right of every page is a bubble icon and badge count indicating the number of changes made to the CDN since the last viewing. Clicking on this expands a short list, with an option to See All Change Logs. Clicking on this will navigate to the “Changelog” page.
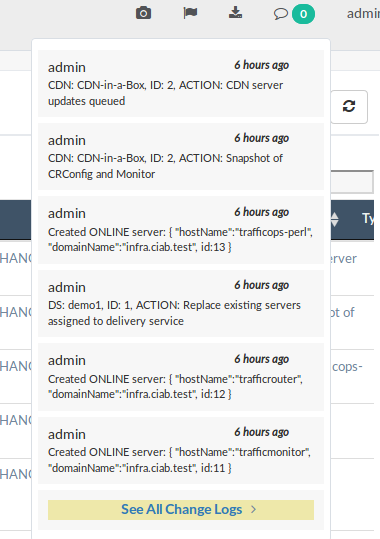
Fig. 5 The Changelog Dialog
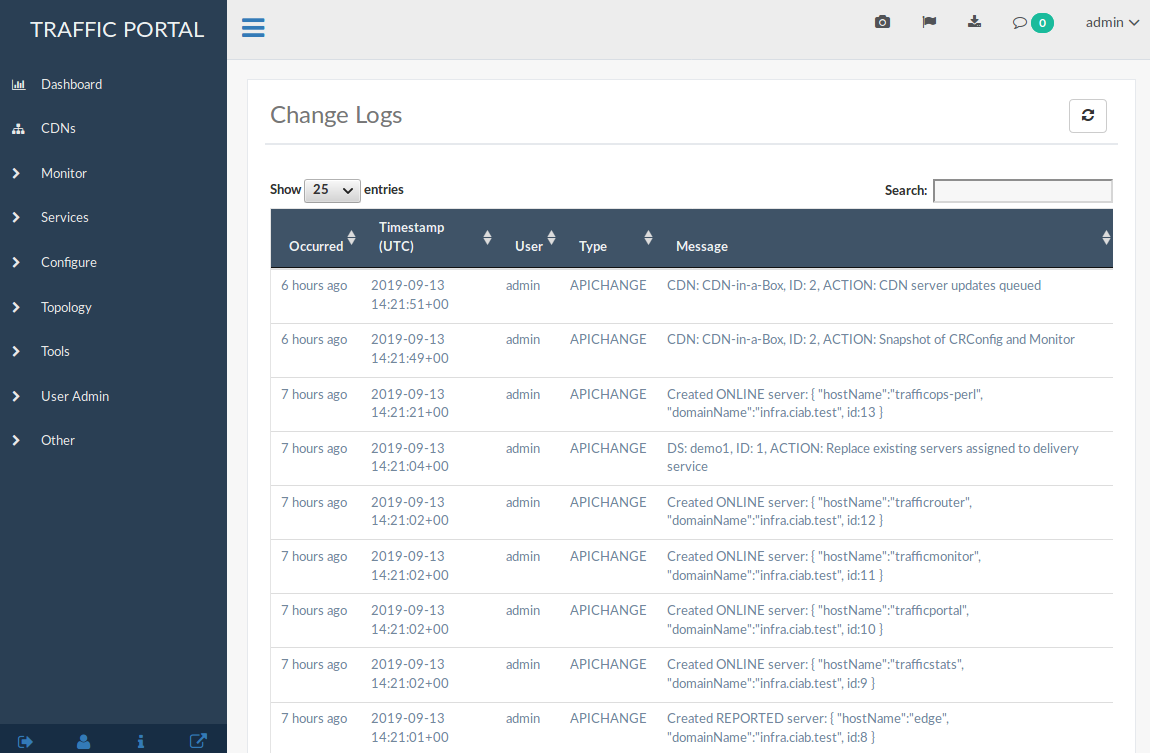
Fig. 6 The Full Change Logs Page
Dashboard
The Dashboard is the default landing page for Traffic Portal. It provides a real-time view into the main performance indicators of the CDNs managed by Traffic Control. It also displays various statistics about the overall health of your CDN.
- Current Bandwidth
The current bandwidth of all of your CDNs.
- Current Connections
The current number of connections to all of your CDNs.
- Healthy Caches
Displays the number of healthy cache servers across all CDNs. Click the link to view the healthy caches on the cache stats page.
- Unhealthy Caches
Displays the number of unhealthy cache servers across all CDNs. Click the link to view the unhealthy caches on the cache stats page.
- Online Caches
Displays the number of cache servers with ONLINE Status. Traffic Monitor will not monitor the state of ONLINE servers.
- Reported Caches
Displays the number of cache servers with REPORTED Status.
- Offline Caches
Displays the number of cache servers with OFFLINE Status.
- Admin Down Caches
Displays the number of caches with ADMIN_DOWN Status.
Each component of this view is updated on the intervals defined in the traffic_portal/app/src/traffic_portal_properties.json configuration file.
CDNs
A table of CDNs with the following columns:
- Name:
The name of the CDN
- Domain:
The CDN’s TLD
- DNSSEC Enabled:
‘true’ if DNSSEC is enabled on this CDN, ‘false’ otherwise.
CDN management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new CDN
update an existing CDN
delete an existing CDN
Queue Updates on all servers in a CDN, or clear such updates
Compare CDN Snapshots
create a CDN Snapshot
manage a CDN’s DNSSEC keys
manage a CDN’s Federations
view Delivery Services of a CDN
view CDN Profiles
view servers within a CDN
Monitor
The Monitor section of Traffic Portal is used to display statistics regarding the various cache servers within all CDNs visible to the user. It retrieves this information through the Traffic Ops API from Traffic Monitor instances.
Fig. 11 The ‘Monitor’ Menu
Cache Checks
A real-time view into the status of each cache server. The page is intended to give an overview of the caches managed by Traffic Control as well as their status.
Warning
Several of these columns may be empty by default - particularly in the CDN in a Box environment - and require Traffic Ops Extensions to be installed/enabled/configured in order to work.
- Hostname:
The (short) hostname of the cache server
- Profile:
The Name of the Profile used by the cache server
- Status:
The Status of the cache server
See also
- UPD:
Displays whether or not this cache server has configuration updates pending
- RVL:
Displays whether or not this cache server (or one or more of its parents) has content invalidation requests pending
- ILO:
Indicates the status of an iLO interface for this cache server
- 10G:
Indicates whether or not the IPv4 address of this cache server is reachable via ICMP “pings”
- FQDN:
DNS check that matches what the DNS servers respond with compared to what Traffic Ops has configured
- DSCP:
Checks the DSCP value of packets received from this cache server
- 10G6:
Indicates whether or not the IPv6 address of this cache server is reachable via ICMP “pings”
- MTU:
Checks the MTU by sending ICMP “pings” from the Traffic Ops server
- RTR:
Checks the reachability of the cache server from the CDN’s configured Traffic Routers
- CHR:
Cache-Hit Ratio (percent)
- CDU:
Total Cache-Disk Usage (percent)
- ORT:
Uses the ORT script on the cache server to determine if the configuration in Traffic Ops matches the configuration on cache server itself. The user as whom this script runs must have an SSH key on each server.
Cache Stats
A table showing the results of the periodic Check Extensions that are run. These can be grouped by Cache Group and/or Profile.
- Profile:
Name of the Profile applied to the Edge-tier or Mid-tier cache server, or the special name “ALL” indicating that this row is a group of all cache servers within a single Cache Group
- Host:
‘ALL’ for entries grouped by Cache Group, or the hostname of a particular cache server
- Cache Group:
Name of the Cache Group to which this server belongs, or the name of the Cache Group that is grouped for entries grouped by Cache Group, or the special name “ALL” indicating that this row is an aggregate across all Cache Groups
- Healthy:
True/False as determined by Traffic Monitor
See also
- Status:
Status of the cache server or Cache Group
- Connections:
Number of currently open connections to this cache server or Cache Group
- MbpsOut:
Data flow rate outward from the CDN (toward client) in Megabits per second
Services
Services groups the functionality to modify Delivery Services - for those users with the necessary permissions - or make Delivery Service Requests for such changes - for users without necessary permissions. Delivery Services can also be grouped by Service Category.
Fig. 12 The ‘Services’ Menu
Delivery Services
This page contains a table displaying all Delivery Services visible to the user as determined by their Tenant.
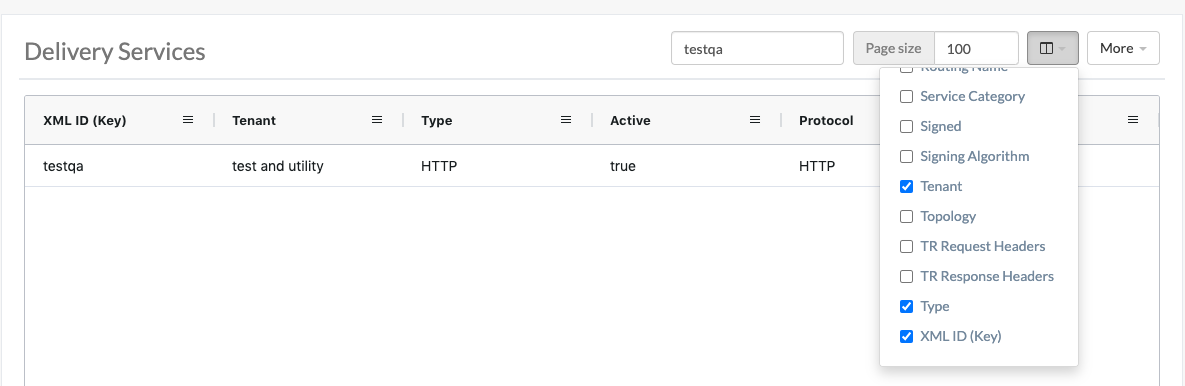
Fig. 13 Table of Delivery Services
Use the Select Columns menu to select the delivery service columns to view and search. Columns can also be rearranged using drag-and-drop. Available delivery service columns include:
Active (visible by default)
CDN (visible by default)
DSCP (visible by default)
IPv6 Routing Enabled (visible by default)
Origin Server Base URL (visible by default)
Protocol (visible by default)
Query String Handling (visible by default)
Signing Algorithm (visible by default)
Tenant (visible by default)
Type (visible by default)
xml_id (visible by default)
Delivery Service management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Create a new Delivery Service
Clone an existing Delivery Service
Update an existing Delivery Service
Delete an existing Delivery Service
Compare Delivery Services
Manage Delivery Service SSL keys
Manage Delivery Service URL signature keys
Manage Delivery Service URI signing keys
Manage Delivery Service invalidation requests
Manage Delivery Service origins
Manage Delivery Service regular expressions
Manage Delivery Service server assignments
Manage Delivery Service steering targets
Manage Delivery Service static DNS records within a Delivery Service subdomain
Test Consistent Hashing Patterns
See also
Delivery Service Requests
If enabled in the traffic_portal_properties.json configuration file, all Delivery Service changes (create, update and delete) are captured as a Delivery Service Request and must be reviewed before fulfillment/deployment.
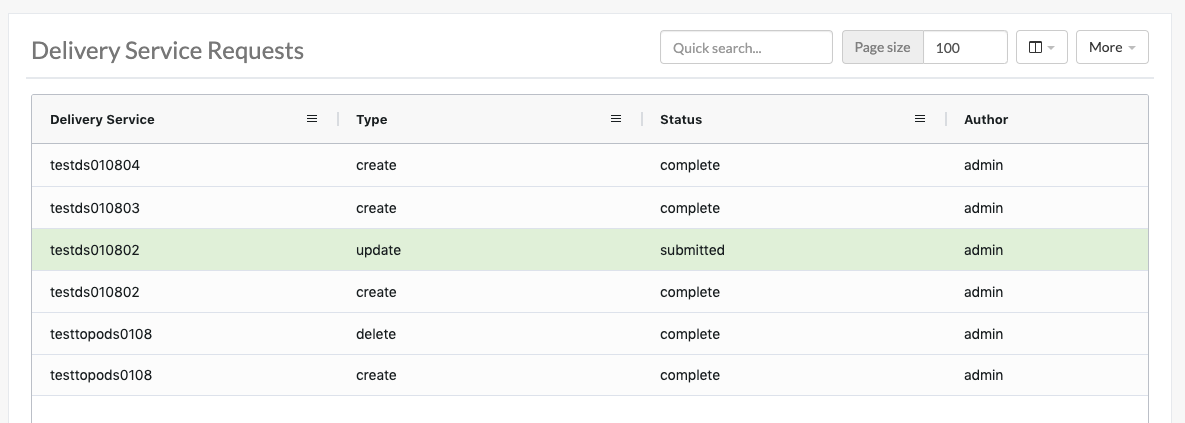
Fig. 14 Table of Delivery Service Requests
Delivery Service: A unique string that identifies the Delivery Service with which the request is associated. This unique string is also known (and ofter referred to within documentation and source code) as a Delivery Service key’ or ‘XML ID’/’xml_id’/’xmlid’ :Type: The type of Delivery Service Request: ‘create’, ‘update’, or ‘delete’ according to what was requested :Status: The status of the Delivery Service Request. Has the following possible values:
- draft
The Delivery Service Request is not ready for review and fulfillment
- submitted
The Delivery Service Request is ready for review and fulfillment
- rejected
The Delivery Service Request has been rejected and cannot be modified
- pending
The Delivery Service Request has been fulfilled but the changes have yet to be deployed
- complete
The Delivery Service Request has been fulfilled and the changes have been deployed
- Author:
The user responsible for creating the Delivery Service Request
- Assignee:
The user responsible for fulfilling the Delivery Service Request. Currently, the operations role or above is required to assign Delivery Service Requests
- Last Edited By:
The last user to edit the Delivery Service Request
- Created:
Relative time indicating when the Delivery Service Request was created
- Actions:
Actions that can be performed on a Delivery Service Request. The following actions are provided:
- fulfill
Implement the changes captured in the Delivery Service Request
- reject
Reject the changes captured in the Delivery Service Request
- delete
Delete the Delivery Service Request
Delivery Service Request management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Delivery Service Request
update an existing Delivery Service Request
delete an existing Delivery Service Request
update the status of a Delivery Service Request
assign a Delivery Service Request
reject a Delivery Service Request
fulfill a Delivery Service Request
complete a Delivery Service Request
See also
Configure
Interfaces for managing the various components of Traffic Control and how they interact are grouped under Configure.
Fig. 15 The ‘Configure’ Menu
Servers
A configurable table of all servers (of all kinds) across all Delivery Services and CDNs visible to the user.
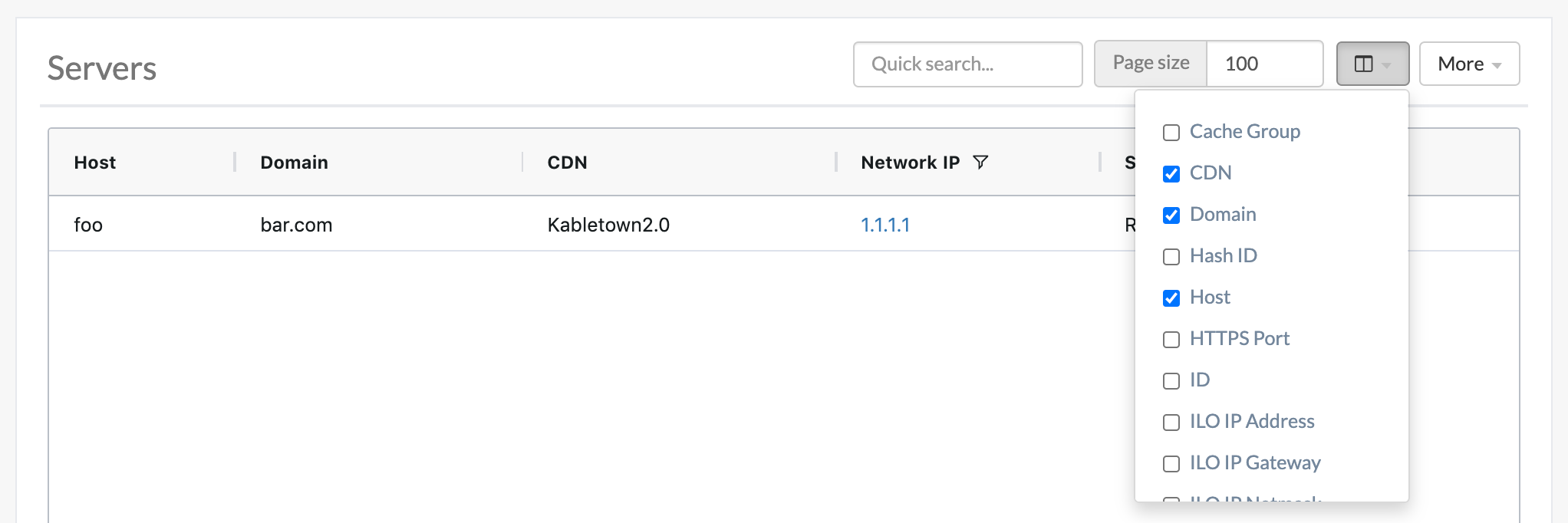
Fig. 16 Table of Servers
Use the Quick Search to search across all table columns or the column filter to apply a more powerful filter to individual columns. Use the Select Columns menu to select the server columns to view. Columns can also be rearranged using drag-and-drop. Available server columns include:
- Cache Group:
[Visible by default] The Name of the Cache Group to which this server belongs
- CDN:
[Visible by default] The name of the CDN to which the server belongs
- Domain:
[Visible by default] The domain part of the server’s FQDN
- Hash ID:
The identifier of the server used in Traffic Router’s consistent hashing algorithm.
- Host:
[Visible by default] The (short) hostname of the server
- HTTPS Port:
The port on which the server listens for incoming HTTPS connections/requests
- ID:
An integral, unique identifier for this server
- ILO IP Address:
The IPv4 address of the server’s ILO service
See also
- ILO IP Gateway:
The IPv4 gateway address of the server’s ILO service
- ILO IP Netmask:
The IPv4 subnet mask of the server’s ILO service
- ILO Username:
The user name for the server’s ILO service
- Interface Name:
The name of the primary network interface used by the server
- IPv6 Address:
[Visible by default] The IPv6 address and subnet mask of
interfaceName- IPv6 Gateway:
The IPv6 address of the gateway used by
interfaceName- Last Updated:
The date and time at which this server description was last modified
- Mgmt IP Address:
The IPv4 address of some network interface on the server used for ‘management’
- Mgmt IP Gateway:
The IPv4 address of a gateway used by some network interface on the server used for ‘management’
- Mgmt IP Netmask:
The IPv4 subnet mask used by some network interface on the server used for ‘management’
- IPv4 Gateway:
The IPv4 address of the gateway used by
interfaceName- IPv4 Address:
[Visible by default] The IPv4 address of
interfaceName- Network MTU:
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) to configured on
interfaceName- IPv4 Subnet:
The IPv4 subnet mask used by
interfaceName- Offline Reason:
A user-entered reason why the server is in ADMIN_DOWN or OFFLINE status
- Phys Location:
The name of the physical location where the server resides
- Profile:
[Visible by default] The Name of the Profile used by this server
- Rack:
A string indicating “server rack” location
- Reval Pending:
[Visible by default] A boolean value represented as a clock (content invalidation/revalidation is pending) or green check mark (content invalidation/revalidation is not pending)
- Router Hostname:
The human-readable name of the router responsible for reaching this server’s interface
- Router Port:
The human-readable name of the port used by the router responsible for reaching this server’s interface
- Status:
[Visible by default] The Status of the server
See also
- TCP Port:
The port on which this server listens for incoming TCP connections
- Type:
[Visible by default] The name of the Type of this server
- Update Pending:
[Visible by default] A boolean value represented as a clock (updates are pending) or green check mark (updates are not pending), typically to be acted upon by Traffic Ops ORT
Server management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Create a new server
Update an existing server
Delete an existing server
Queue Updates on a server, or clear such updates
Update server status
View server Delivery Services
Clone Delivery Service assignments
Assign Delivery Services to server(s)
Origins
A table of all Origins. These are automatically created for the Origins served by Delivery Services throughout all CDNs, but additional ones can be created at will. The table has the following columns:
- Name:
The name of the Origin. If this Origin was created automatically for a Delivery Service, this will be the xml_id of that Delivery Service.
- Tenant:
The name of the Tenant that owns this Origin - this is not necessarily the same as the Tenant that owns the Delivery Service to which this Origin belongs.
- Primary:
Either
trueto indicate that this is the “primary” Origin for the Delivery Service to which it is assigned, orfalseotherwise.- Delivery Service:
The xml_id of the Delivery Service to which this Origin is assigned.
- FQDN:
The FQDN of the Origin.
- IPv4 Address:
The Origin’s IPv4 address, if configured.
- IPv6 Address:
The Origin’s IPv6 address, if configured.
- Protocol:
The protocol this Origin uses to serve content. One of
http
https
- Port:
The port on which the Origin listens for incoming HTTP(S) requests.
Note
If this field appears blank in the table, it means that a default was chosen for the Origin based on its Protocol -
80for “http”,443for “https”.- Coordinate:
The name of the geographic coordinate pair that defines the physical location of this Origin. Origins created for Delivery Services automatically will not have associated Coordinates. This can be rectified on the details pages for said Origins
- Cachegroup:
The Name of the Cache Group to which this Origin belongs, if any.
- Profile:
Origin management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Profiles
A table of all Profiles. From here you can see Parameters, servers and Delivery Services assigned to each Profile. Each entry in the table has these fields:
- Name:
- Type:
The Type of this Profile, which indicates the kinds of objects to which the Profile may be assigned
- Routing Disabled:
The Routing Disabled setting of this Profile
- Description:
This Profile’s Description
- CDN:
The CDN to which this Profile is restricted. To use the same Profile across multiple CDNs, clone the Profile and change the clone’s CDN field.
Profile management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Profile
update an existing Profile
delete an existing Profile
clone a Profile
export a Profile
view Profile Parameters
view Profile Delivery Services
view Profile servers
Parameters
This page displays a table of Parameters from all Profiles with the following columns:
- Name:
- Config File:
The Config File to which the Parameter belongs.
- Value:
- Secure:
- Profiles:
Parameter management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Types
Types group Delivery Services, servers and Cache Groups for various purposes. Each entry in the table shown on this page has the following fields:
- Name:
The name of the Type
- Use In Table:
States the use of this Type, e.g.
serverindicates this is a Type assigned to servers- Description:
A short, usually user-defined, description of the Type
Type management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Type
update an existing Type
delete an existing Type
view Delivery Services assigned to a Type
view servers assigned to a Type
view Cache Groups assigned to a Type
Statuses
This page shows a table of Statuses with the following columns:
- Name:
The name of this Status
- Description:
A short, usually user-defined, description of this Status
Status management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Topology
Topology groups views and functionality that deal with how CDNs and their Traffic Control components are grouped and distributed, both on a logical level as well as a physical level.
Fig. 17 ‘Topology’ Menu
Cache Groups
This page is a table of Cache Groups, each entry of which has the following fields:
- Name:
The full Name of this Cache Group
- Short Name:
- Type:
This Cache Group’s Type
- Latitude:
- Longitude:
Cache Group management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Cache Group
update an existing Cache Group
delete an existing Cache Group
Queue Updates for all servers in a Cache Group, or clear such updates
view Cache Group ASNs
view and assign Cache Group Parameters
view Cache Group servers
Coordinates
allows a label to be given to a set of geographic coordinates for ease of use. Each entry in the table on this page has the following fields:
- Name:
The name of this coordinate pair
- Latitude:
The geographic latitude part of the coordinate pair
- Longitude:
The geographic longitude part of the coordinate pair
Coordination management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new coordinate pair
update an existing coordinate pair
delete an existing coordinate pair
Phys Locations
A table of Physical Locations which may be assigned to servers and Cache Groups, typically for the purpose of optimizing client routing. Each entry has the following columns:
- Name:
The full name of the Physical Location
- Short Name:
A shorter, more human-friendly name for this Physical Location
- Address:
The Physical Location’s street address (street number and name)
- City:
The city within which the Physical Location resides
- State:
The state within which the Physical Location’s city lies
- Region:
The Region to which this Physical Location has been assigned
Physical Location management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Physical Location
update an existing Physical Location
delete an existing Physical Location
view Physical Location servers
Divisions
Each entry in the table of Divisions on this page has the following fields:
- Name:
The name of the Division
Division management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Regions
Each entry in the table of Regions on this page has the following fields:
Region management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Region
update an existing Region
delete an existing Region
view Physical Locations within a Region
ASNs
Manage ASNs. Each entry in the table on this page has the following fields:
- ASN:
The actual ASN
- Cache Group:
The Cache Group to which this ASN is assigned
ASN management includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new ASN
update an existing ASN
delete an existing ASN
Tools
Tools contains various tools that don’t directly relate to manipulating Traffic Control components or their groupings.
Fig. 18 The ‘Tools’ Menu
Invalidate Content
Here, specific assets can be invalidated in all caches of a Delivery Service, forcing content to be updated from the origin. Specifically, this doesn’t mean that cache servers will immediately remove items from their caches, but rather will fetch new copies whenever a request is made matching the ‘Asset URL’ regular expression. This behavior persists until the Content Invalidation Job’s TTL expires.
Warning
This method forces cache servers to “re-validate” content, so in order to work properly the Origin needs to support revalidation according to section 4.3.2 of RFC 7234.
Each entry in the table on this page has the following fields:
- Delivery Service:
The Delivery Service to which to apply this Content Invalidation Job
- Asset URL:
A URL or regular expression which describes the asset(s) to be invalidated
- TTL (Hours):
A TTL (as a number of hours) over which the Content Invalidation Job shall remain active
- Start:
An effective start time until which the job is delayed
- Expires:
The date/time at which the Content Invalidation Job will end (effectively “Start” plus “TTL (Hours)”)
- Created By:
The user name of the person who created this Content Invalidation Job
- Invalidation Type:
The Invalidation Type of this Content Invalidation Job
Invalidate content includes the ability to (where applicable):
create a new Content Invalidation Job
Generate ISO
Generates a boot-able system image for any of the servers in the Servers table (or any server for that matter). Currently it only supports CentOS 7, but if you’re brave and pure of heart you MIGHT be able to get it to work with other Unix-like Operating Systems. The interface is mostly self-explanatory, but here is a short explanation of the fields in that form.
See also
For instructions on setting up the Kickstart ISO generation files, see Creating the CentOS Kickstart File.
- Copy Server Attributes From
Optional. This option lets the user choose a server from the Traffic Ops database and will auto-fill the other fields as much as possible based on that server’s properties
- OS Version
This list is populated by modifying the
osversions.jsonfile on the Traffic Ops server. This file maps OS names to the name of a directory under kickstart.files.location (/var/www/filesby default).- Hostname
The desired hostname of the resultant system
- Domain
The desired domain name of the resultant system
- DHCP
If this is ‘no’ the IP settings of the system must be specified, and the following extra fields will appear:
- IP Address
The resultant system’s IPv4 address
- IPv6 Address
The resultant system’s IPv6 address
- Network Subnet
The system’s network subnet mask
- Network Gateway
The system’s network gateway’s IPv4 address
- IPv6 Gateway
The system’s network gateway’s IPv6 address
- Management IP Address
An optional IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) of a “management” server for the resultant system (e.g. for ILO)
- Management IP Netmask
The subnet mask (IPv4 or IPv6) used by a “management” server for the resultant system (e.g. for ILO) - only needed if the Management IP Address is provided
- Management IP Gateway
The IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) of the network gateway used by a “management” server for the resultant system (e.g. for ILO) - only needed if the Management IP Address is provided
- Management Interface
The network interface used by a “management” server for the resultant system (e.g. for ILO) - only needed if the Management IP Address is provided. Must not be the same as “Interface Name”.
- Network MTU
The system’s network’s MTU. Despite being a text field, this can only be 1500 or 9000 - it should almost always be 1500
- Disk for OS Install
The disk on which to install the base system. A reasonable default is
sda(the/dev/prefix is not necessary)- Root Password
The password to be used for the root user. Input is hashed using MD5 before being written to disk
- Confirm Root Password
Repeat the ‘Root Password’ to be sure it’s right
- Interface Name
Optional. The name of the resultant system’s network interface. Typical values are
bond0,eth4, etc. Ifbond0is entered, a Link Aggregation Control Protocol bonding configuration will be writtenSee also
- Stream ISO
If this is ‘yes’, then the download will start immediately as the ISO is written directly to the socket connection from Traffic Ops. If this is ‘no’, then the download will begin only after the ISO has finished being generated. For almost all use cases, this should be ‘yes’.
Implementation Detail
Traffic Ops uses Red Hat’s Kickstart <https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/installation_guide/chap-kickstart-installations> to create these ISOs, so many configuration options not available here can be tweaked in the Kickstart configuration file.
User Admin
This section offers administrative functionality for users and their permissions.
Fig. 19 The ‘User Admin’ Menu
User
This page lists all the users that are visible to the user (so, for ‘admin’ users, all users will appear here). Each entry in the table on this page has the following fields:
- Full Name:
The user’s full, real name
- Username:
The user’s username
- Email:
The user’s email address
- Tenant:
The user’s Tenant
- Role:
The user’s Role
User management includes the ability to (where applicable):
register a new user
create a new user
update an existing user
view Delivery Services visible to a user
Note
If OAuth is enabled, the username must exist both here as well as with the OAuth provider. A user’s rights are defined by the Role assigned to the user in Traffic Ops. Creating/deleting a user here will update the user’s Role but the user needs to be created/deleted with the OAuth provider as well.
Tenants
Each entry in the table of Tenants on this page has the following entries:
- Name:
The name of the Tenant
- Active:
If ‘true’ users of this Tenant group are allowed to login and have active Delivery Services
- Parent:
The parent of this Tenant. The default is the ‘root’ Tenant, which has no users.
Tenant management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Roles
Each entry in the table of Roles on this page has the following fields:
- Name:
The name of the Role
- Privilege Level:
The privilege level of this Role. This is a whole number that actually controls what a user is allowed to do. Higher numbers correspond to higher permission levels
- Description:
A short description of the Role and what it is allowed to do
Role management includes the ability to (where applicable):
Note
Roles cannot be deleted through the Traffic Portal UI
Other
Custom menu items. By default, this contains only a link to the Traffic Control documentation.
Fig. 20 The ‘Other’ Menu
Docs
This is just a link to the Traffic Control Documentation.